 Lycopene is a carotenoid, which is a pigment that can be synthesized by plants but not animals. It has a bright red color and is named after the tomato plant, known scientifically as Solanum lycopersicum. Lycopene was first isolated in 1910 from the fruit of the tomato plant, which has the highest lycopene content of any food commonly available in the West. The molecular structure of lycopene was determined by 1931.
Lycopene is a carotenoid, which is a pigment that can be synthesized by plants but not animals. It has a bright red color and is named after the tomato plant, known scientifically as Solanum lycopersicum. Lycopene was first isolated in 1910 from the fruit of the tomato plant, which has the highest lycopene content of any food commonly available in the West. The molecular structure of lycopene was determined by 1931.
Tomatoes and tomato products provide over 85 percent of the lycopene intake for people in western countries. Additional sources of lycopene include autumn olives, pink guava, pink grapefruit, wolfberries and rosehips.
The most important use of lycopene in plants is to help support the skin’s ability to manage the effects of sunlight. It is also an approved food coloring in most countries due to its strong color and non-toxicity. Lycopene is an antioxidant that provides a variety of supporting functions in humans. It is found in most human tissues, although the tissues with the greatest concentration of lycopene include the blood, skin, adrenal glands and liver.
Lycopene provides a number of health benefits, particularly due to its antioxidant properties. It may help maintain skin health and support the cardiovascular system. It also provides additional health support for the eye, lungs and prostate gland.
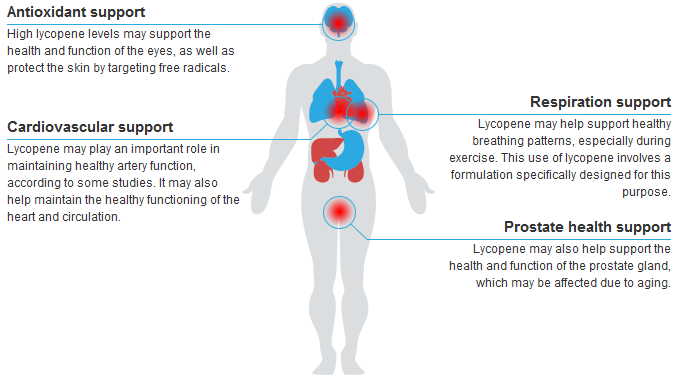
High lycopene levels may support the health and function of the eyes, as well as protect the skin by targeting free radicals.
Lycopene may play an important role in maintaining healthy artery function, according to some studies. It may also help maintain the healthy functioning of the heart and circulation.
Lycopene may help support healthy breathing patterns, especially during exercise. This use of lycopene involves a formulation specifically designed for this purpose.
Lycopene may also help support the health and function of the prostate gland, which may be affected due to aging.
Low levels of carotenoids such as lycopene leave cells vulnerable to damage from free radicals, which are highly reactive with other compounds. Lycopene is especially beneficial in maintaining the cell membrane in the presence of free radicals. The most common signs of a lycopene deficiency include poor health of the heart, lungs and prostate gland. A lycopene deficiency can also cause low energy levels and difficulty maintaining a healthy cholesterol profile.

What are antioxidants? First, it is important to define antioxidants. Despite the fact you get to hear or read a lot about them, the chances are high you have not come across an article or even a podcast wherein a person explained what an antioxid...

Antioxidant Support Astaxanthin Background and Benefits Astaxanthin is a type of carotenoid known as a xanthophyll, which is a pigment that gives plants a red-pink color. It also gives many animals their color, including birds and some shellfish. Dr. Basil Weedon headed the group that first synth...

Metabolism, Heart Health, Bone Strength & Cell Energy Magnesium Background and Benefits Magnesium, a metal, is the ninth most abundant element in the universe. It is named after a region in Greece called Magnesia, where magnesium ores were first discovered. It was isolated in 1808 by Sir Hump...
Shipping calculated at checkout