
Tocotrienols are members of the vitamin E family which play a pivotal antioxidant role in the body. They are transported around your system attached to the Lipoproteins - the complex particles that transport your crucial cholesterol, responsible for creating and repairing all of your body's cells.
Tocotrienols prevent the Lipoproteins from becoming damaged or oxidized and are also delivered all over your body to do the same for your other tissues.
Their strong antioxidant effect prevents your cholesterol from becoming part of the calcification problem, where the "bad" LDL cholesterol can build up on the walls of your blood vessels (called "plaque"). In a sense they work like statin drugs - but without the side effects.
Tocotrienols have a range of other benefits, including working to directly improve your cholesterol profile and reduce triglycerides.
Sadly, buying the vitamin E supplements that are currently sold in the stores doesn't guarantee you get all the benefits of tocotrienols. Rather, most of these vitamin E products overwhelmingly contain the cheaper, easy-to-produce Tocopherols, which are another component of vitamin E.
Not only are tocopherols of very limited value but also, they also interfere with the benefits of any tocotrienols that are present.
The crucial solution is to create a tocotrienol-only product. And Xtend-Life found it - in fact the only pure one available in the world. It is called DeltaGold® and is extracted from Annatto beans and produced in the USA.
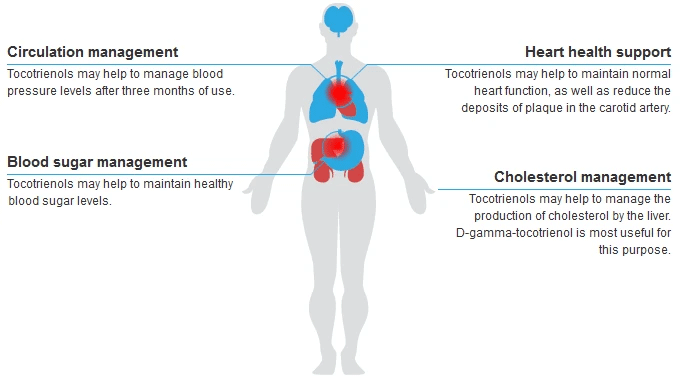
Tocotrienols may help to manage blood pressure levels after three months of use.
Tocotrienols may help to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Tocotrienols may help to maintain normal heart function, as well as reduce the deposits of plaque in the carotid artery.
Tocotrienols may help to manage the production of cholesterol by the liver. D-gamma-tocotrienol is most useful for this purpose.
In this video, one of Xtendlife's researchers, Ivor Cummins, interviews Dr. Barrie Tan covering all things vitamin E, in particular the role it plays in cardiovascular health.
Ivor is a researcher holding several positions, including Chief Program Officer for Irish Heart Disease Awareness. Dr. Tan has a Ph. D. in Chemistry / Biochemistry and is considered one of the world's foremost experts on vitamin E.

In our pursuit of vibrant health, many of us strive for a balanced diet packed with nutrient-rich foods. However, even the most wholesome diet may still leave us lacking in essential nutrients, particularly Omega-3 fatty acids. Healthy Eating is O...
Shipping calculated at checkout